4G industrial router L2TP penetration
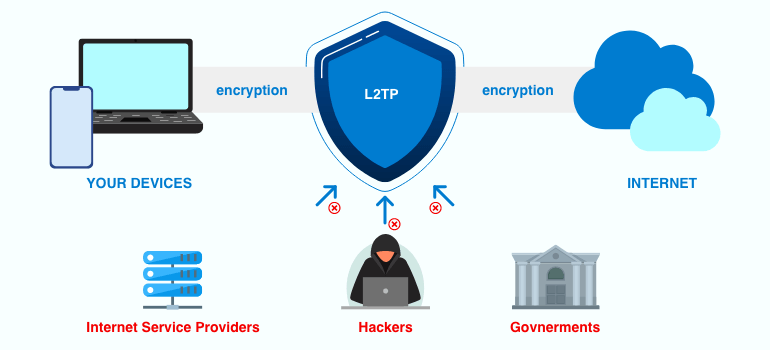
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a network protocol used to support virtual private networks (VPNs) by tunneling data packets between networks. It was developed as a combination of Cisco’s Layer 2 Forwarding Protocol (L2F) and Microsoft’s Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP), making it compatible with various networking environments and systems.
L2TP’s primary purpose is to create secure and private communication channels over public networks, such as the internet, by encapsulating data packets and tunneling them to another network.
A 4G router is a device that connects to a mobile network to provide internet access and can integrate L2TP to manage network traffic and provide a secure connection over a cellular network. Because L2TP uses a specific port (usually UDP 1701) and the GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation) protocol, NAT devices can sometimes block or modify these traffic, causing the VPN connection to fail. The L2TP traversal feature ensures that these VPN traffic can pass through the router smoothly, thus establishing a stable L2TP VPN connection.
Why is L2TP traversal critical for network security and management?
1. Enhanced remote access security: L2TP is often used in conjunction with IPsec to provide encrypted, secure network access to remote users. L2TP traversal allows users to successfully establish VPN connections even in NAT environments, thereby protecting the transmission of sensitive data and enhancing network security.
2. Seamless network management: By supporting L2TP traversal, network administrators can simplify the management of multiple branch offices or remote employees. This allows them to securely access internal resources through a VPN connection, manage remote networks, and guarantee the overall availability and security of the network.
3. User Experience Optimization: For users who rely on L2TP VPN, L2TP pass-through ensures the stability and availability of VPN connections, especially in home or public networks, reducing connection interruptions or latency issues.
4. Broad compatibility: Enabling L2TP traversal in 4G routers ensures that VPN traffic can be transmitted normally even in complex NAT or multi-layer firewall architectures, which makes the network system more compatible and flexible.
Overall, L2TP traversal in 4G routers is essential to ensure the reliability of VPN connections, enhance remote secure access, and simplify network management.
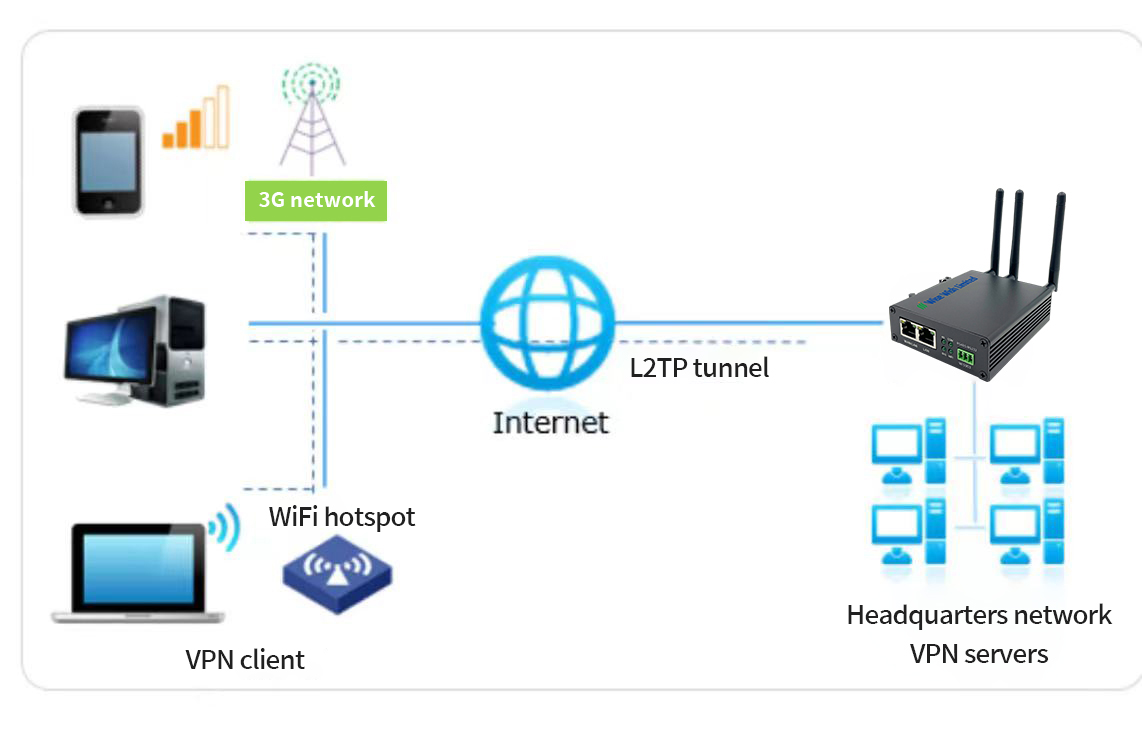
How does a 4G router achieve L2TP penetration?
Implementing L2TP traversal (infiltration) in a 4G router often requires ensuring that the router can properly handle traffic interactions between L2TP and NAT devices, especially in the presence of firewalls or Network Address Translation (NAT). Here are the steps and some key features or settings to enhance its effectiveness:
1. Configure NAT settings:
Configure NAT to support the forwarding of L2TP traffic, as NAT in the router usually affects the normal transmission of L2TP VPN traffic. In order for L2TP traffic to pass through NAT, make sure that NAT is configured to support L2TP traffic forwarding.
2. Open the necessary ports:
Open ports to allow L2TP VPN connections to be established smoothly, the L2TP protocol typically uses UDP 1701 port, and when used in conjunction with IPsec, UDP 500 (for IKE) and UDP 4500 (for NAT traversal) also need to be opened,
3. Adjust Firewall Rules:
Configure rules that allow L2TP and related protocol traffic to prevent L2TP connections from being intercepted by mistake. In particular, the firewall’s Stateful Packet Inspection (SPI) mechanism is checked and adjusted to ensure that legitimate L2TP sessions are not blocked.
4. Enable IPsec support (optional):
If L2TP is used in conjunction with IPsec, make sure the router supports IPsec VPN and has the appropriate features enabled. In addition, you need to configure IPsec-related settings of the router, such as Security Association (SA) and encryption algorithms, to ensure the security of VPN traffic.
Specific features or settings that enhance the effectiveness of L2TP penetration
1. UDP Encapsulation:
4G routers support encapsulating the control and data lanes of L2TP in UDP so that NAT can handle them. This UDP encapsulation method ensures that L2TP traffic can pass through NAT smoothly and improves the stability of L2TP penetration.
2. NAT Traversal (NAT-T) function:
The router supports the NAT Traversal (NAT-T) protocol, which can solve the common problems of IPsec VPN in NAT environment and help L2TP VPN establish connections in complex network structures.
3. QoS (Quality of Service) Settings:
QoS rules can be configured in the router to prioritize L2TP or IPsec traffic. This helps to avoid bandwidth usage by other applications, ensuring the stability and low latency of VPN traffic.
4. Auto reconnect and keep-alive function:
Supports auto-reconnect or keep-alive functionality, which is especially important in mobile environments. This feature can automatically maintain or re-establish the L2TP connection when the network signal is weak or switched (such as when the 4G network is switched to Wi-Fi or other networks), reducing the user’s manual intervention.

brief summary
The correct configuration of NAT on 4G routers, opening necessary ports, and adjusting firewall rules ensure that users can establish secure and stable VPN connections even in NAT and complex network environments, protect data security, and improve the flexibility of network management.
Test the L2TP penetration function
The purpose of this test is to evaluate whether the L2TP traversal function of a 4G router can provide a secure and stable L2TP-based VPN connection.
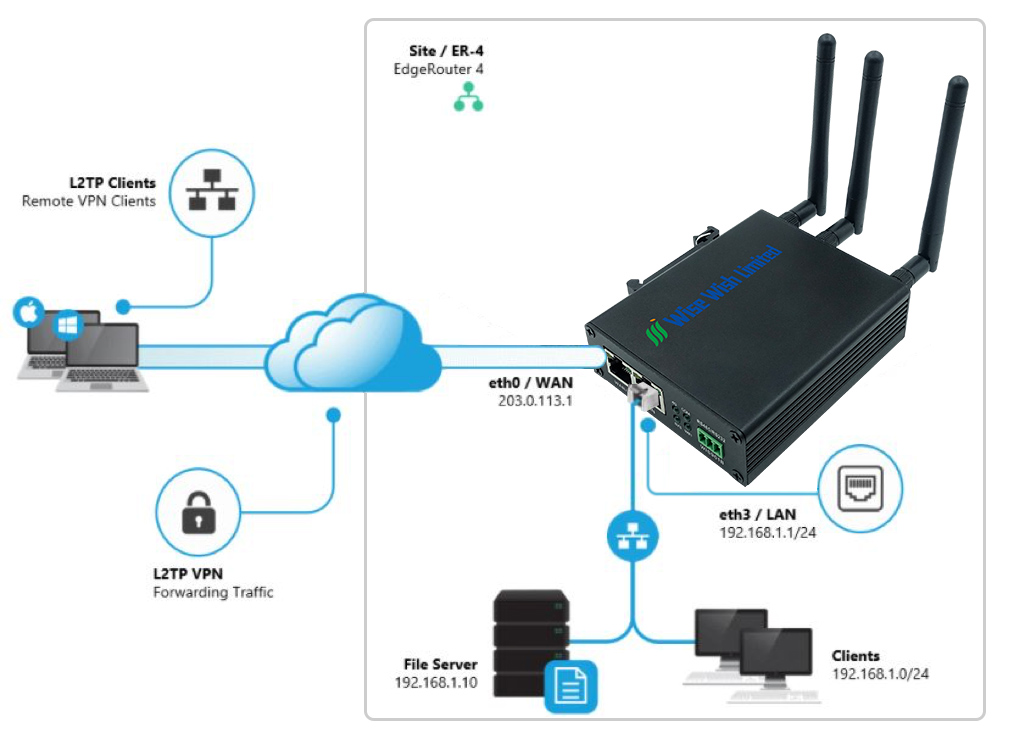
1. Test the environment
VPN server: Enabled
Router: Huizhi Technology’s 4G router
Network Configuration:
PC1 connects to the VPN server through the public IP of the VPN server
PC2 connects to Huizhi Technology’s 4G router and connects to the VPN server through the public IP of the VPN server
2. Test scenario:
4G routers disable L2TP traversal and make L2TP-based VPN connections
The 4G router enables L2TP traversal and makes an L2TP-based VPN connection
The 4G router enables L2TP traversal and makes long-term L2TP-based VPN connections
3. Test steps
Enable or Disable L2TP Traversal: Log in to the router’s web interface, navigate to the Firewall System Security page, and enable or disable L2TP Traversal
VPN connection: The PC connects to the VPN server to establish an L2TP-based VPN connection
Test the connection: By ping the test, using the command line interface to ping the other instance, PC2 ping the PC1 virtual IP address will verify the connection between the L2TP client and the server.
4. Test results
The 4G router disables L2TP traversal and makes L2TP-based VPN connections, but PC2 cannot connect to the VPN server, which proves that the device cannot make L2TP-based VPN connections when L2TP traversal is disabled on the 4G router.

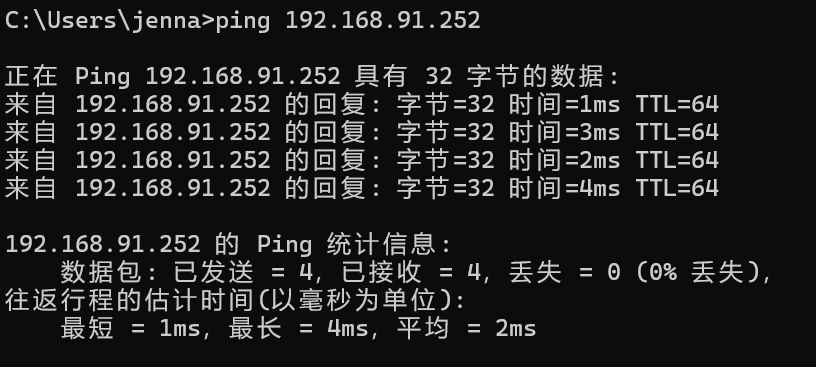
The 4G router enables L2TP traversal and conducts an L2TP-based VPN connection, PC2 can connect to the VPN server, the virtual IP address is 192.168.90.250, and the virtual IP address of PC1 is 192.168.90.252, which can ping, proving that the 4G router can provide L2TP-based VPN connection with L2TP traversal enabled.
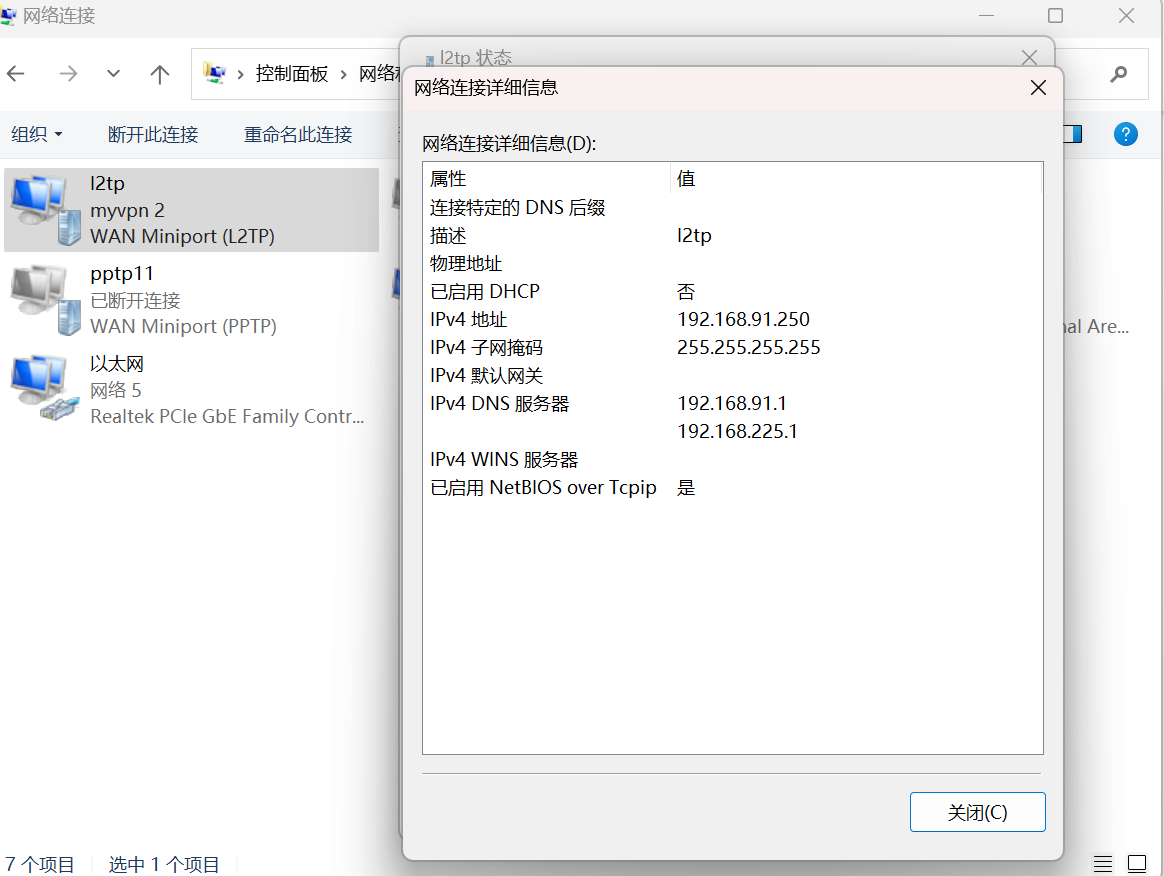
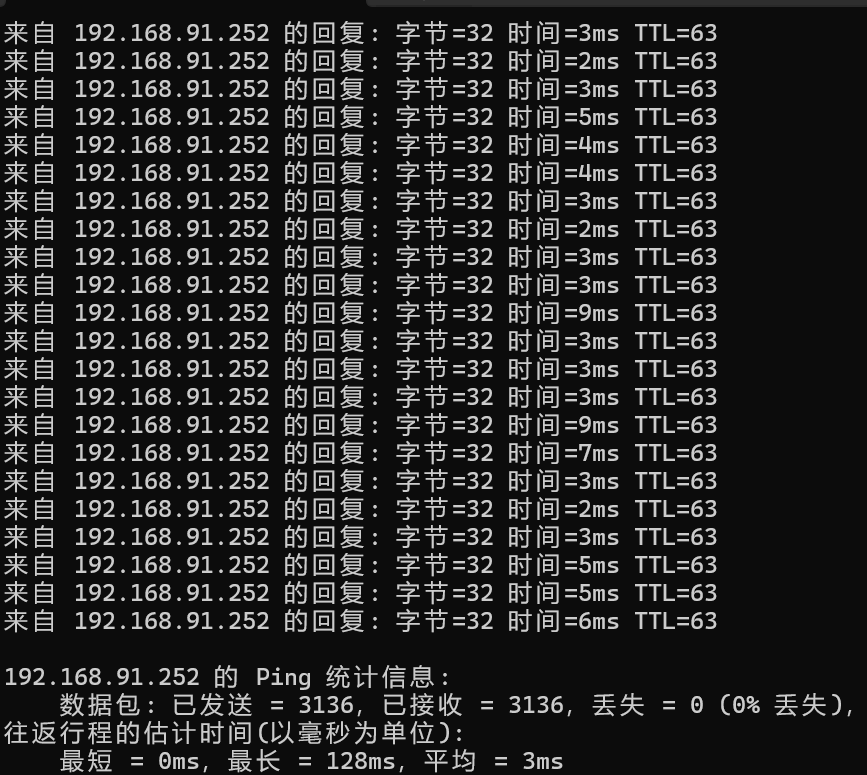
The 4G router enables L2TP traversal and conducts L2TP-based VPN connections for a long time, PC2 is able to connect to the VPN server, the virtual IP address is 192.168.90.250, PC2 pings the virtual IP address of PC1 for a long time 192.168.90.252, and PC2 is able to ping PC1 for a long time, which proves that the 4G router can provide a long-term and stable L2TP-based VPN connection with L2TP traversal enabled.
Summary
L2TP plays an important role in 4G routers because it is able to establish secure tunnel connections between different sites, ensuring the secure transmission of data. Especially in the field of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), where there is an increasing need for device connectivity and data transmission, L2TP protects the confidentiality and integrity of data by providing strong encryption and authentication functions in combination with IPsec. In addition, as a gateway device for inter-site communication, Huizhi Technology’s 4G router supports the L2TP protocol, which can enable and disable L2TP penetration independently, flexibly respond to the connection needs in the mobile network environment, and improve the security and stability of the network.

