
DC Charger networking: 4G industrial router vs 4G module
Have you ever encountered issues such as frequent network disconnections, remote control failures, or even transaction failures caused by unstable signals during the operation of DC charging piles? The root cause may lie in the choice of networking solution. Why do most DC charging pile manufacturers tend to use 4G industrial routers rather than directly integrating 4G modules? The answer involves deeper differences in stability, security, and operational efficiency.
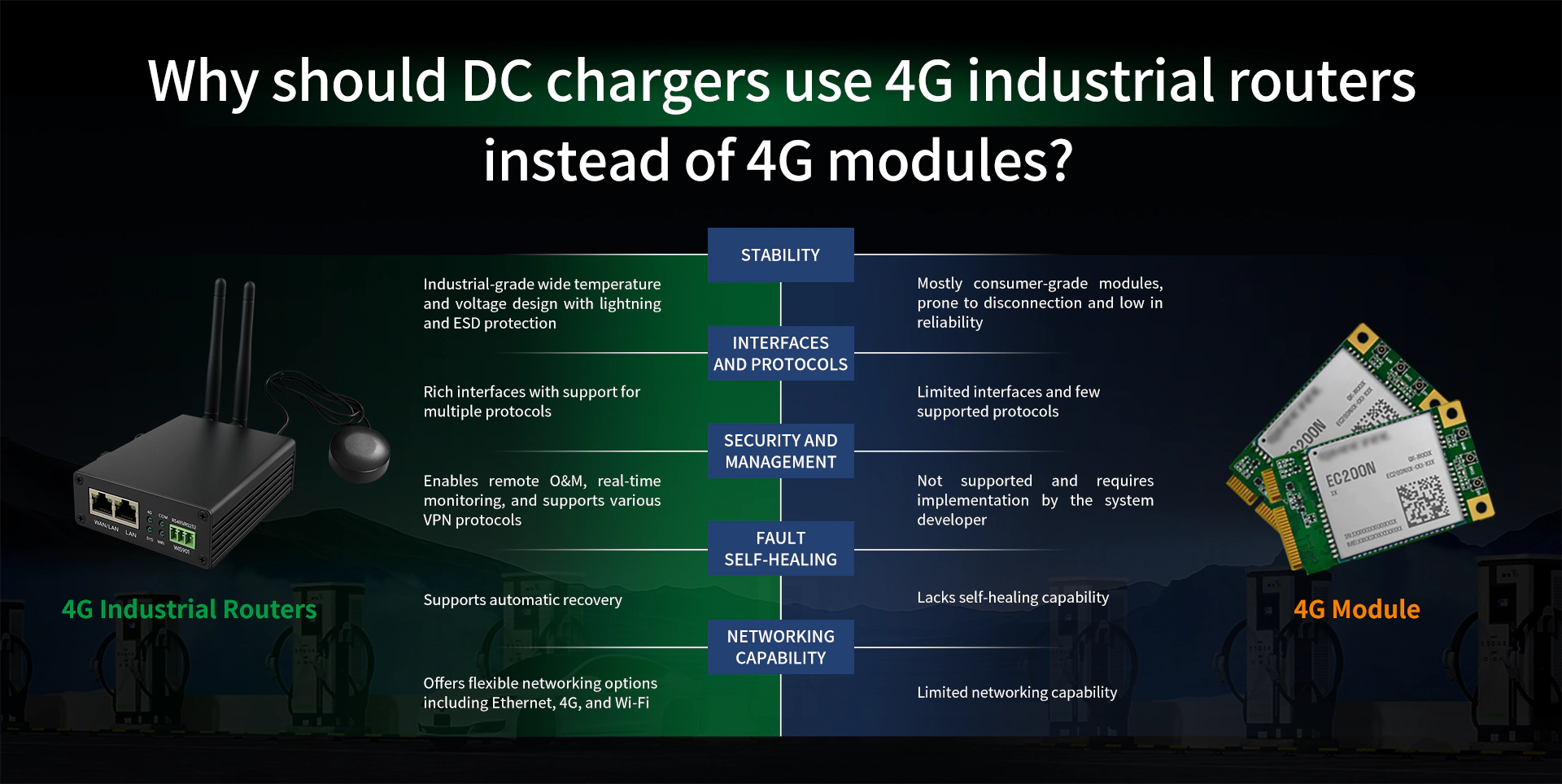
▶ 1. Industrial-Grade Stability and Reliability
- 4G industrial routers are built with industrial-grade design, featuring wide temperature tolerance and high protection ratings. They can operate stably for long periods in harsh environments, making them suitable for outdoor and unattended scenarios.
- 4G modules are generally consumer-grade or embedded products that only provide basic networking functions. Their resistance to interference, temperature extremes, and continuous operation is weak, making them prone to communication interruptions due to environmental changes.
▶ 2. Multiple Interfaces and Protocol Support
- Industrial routers typically integrate multiple interfaces (such as RS485, Ethernet, Wi-Fi) and can connect multiple devices simultaneously. They support various protocols (like Modbus), facilitating unified management of charging piles from different brands or types.
- 4G modules have single, mostly serial interfaces and limited expandability, making it difficult to meet the complex data collection and management needs of DC charging piles.
▶ 3. Network Security and Remote Management
- Industrial routers support multiple VPN protocols (such as OpenVPN and IPSEC) to ensure data transmission security. They also enable remote configuration, monitoring, and firmware upgrades, greatly improving maintenance efficiency.
- 4G modules have simple security mechanisms and limited remote management functions, making them inadequate for the maintenance and security needs of large-scale charging pile deployments.
▶ 4. Fault Self-Diagnosis and Automatic Recovery
- Industrial routers feature self-diagnosis and auto-reconnection, allowing them to automatically recover from network anomalies and ensure continuous connectivity for charging piles.
- 4G modules usually lack intelligent self-healing capabilities, are prone to disconnection during network fluctuations, and require manual intervention.
▶ 5. Multi-Device Access and Scalability
- Industrial routers can provide network sharing (via LAN/Wi-Fi) for multiple devices such as the charging pile controller, display screens, and cameras, saving on hardware costs.
- 4G modules support only single-device networking and have poor scalability.
▶ Conclusion
Choosing a networking solution for DC charging piles is essentially a trade-off between short-term costs and long-term reliability. While 4G modules are cheaper, they may pose hidden risks in maintenance, security, and scalability. 4G industrial routers, with their stable connectivity, robust protection, and remote management capabilities, have become the mainstream choice in the industry.